The Template Method Design Pattern in PHP is a behavioral pattern that defines the skeleton of an algorithm in a base class and allows subclasses to redefine certain steps without changing the overall structure. If you want to control workflow while keeping your code flexible and clean, this pattern in PHP is a powerful solution. It helps you enforce consistency, reduce duplication, and maintain open/closed principle compliance in real-world applications.
In simple terms, this pattern locks the process but lets child classes customize specific parts. It is especially useful when multiple classes follow the same process but differ in certain steps.
What Is the Template Method Design Pattern in PHP?
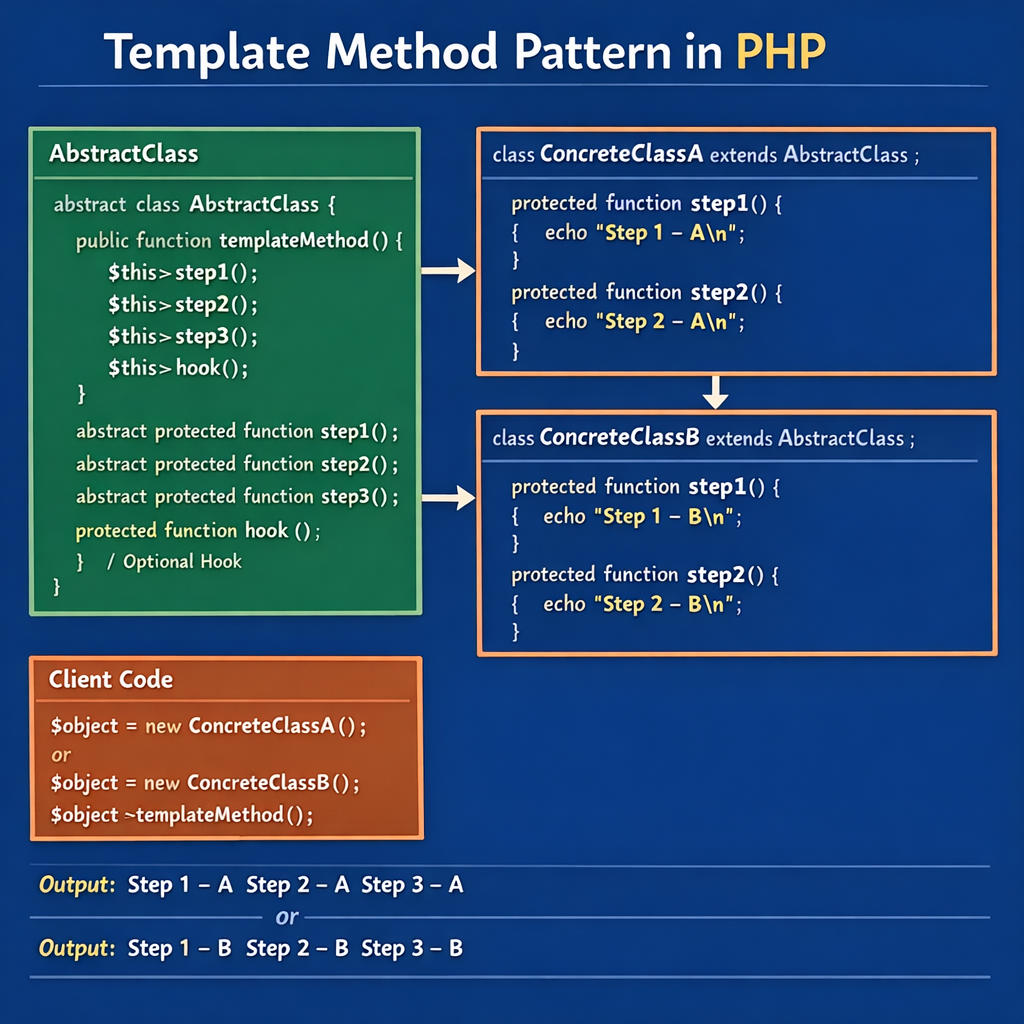
The Template Method pattern defines an algorithm inside a base class method (called the template method). Some steps are implemented directly in the base class, while others are declared abstract so subclasses must provide their own implementation.
Core Idea
- Create an abstract base class.
- Define a final template method that outlines the workflow.
- Declare abstract methods for steps that vary.
- Let subclasses implement those variable steps.
This ensures the overall algorithm structure never changes.
When to Use Template Method Design Pattern in PHP?
Use this pattern when:
- Multiple classes share a similar workflow.
- Only certain steps differ.
- You want to avoid code duplication.
- You need strict control over execution order.
For example:
- Data export systems (CSV, JSON, XML).
- Payment processing pipelines.
- Report generation engines.
- Authentication flows.
Without Template Method Design Pattern in PHP
Here is a poorly structured approach:
class CsvExporter
{
public function export(array $data): void
{
echo "Connecting to database...\n";
echo "Formatting data as CSV...\n";
echo "Saving CSV file...\n";
echo "Disconnecting from database...\n";
}
}
class JsonExporter
{
public function export(array $data): void
{
echo "Connecting to database...\n";
echo "Formatting data as JSON...\n";
echo "Saving JSON file...\n";
echo "Disconnecting from database...\n";
}
}
Why This Is Bad?
- Code duplication.
- Hard to maintain.
- Any workflow change requires editing multiple classes.
- Violates DRY principle.
If tomorrow you add logging, you must update every class.
Template Method Design Pattern in PHP
Now let’s refactor using the Template Method Design Pattern in PHP.
abstract class DataExporter
{
final public function export(array $data): void
{
$this->connect();
$this->format($data);
$this->save();
$this->disconnect();
}
protected function connect(): void
{
echo "Connecting to database...\n";
}
protected function disconnect(): void
{
echo "Disconnecting from database...\n";
}
abstract protected function format(array $data): void;
abstract protected function save(): void;
}
Concrete Implementations
class CsvExporter extends DataExporter
{
protected function format(array $data): void
{
echo "Formatting data as CSV...\n";
}
protected function save(): void
{
echo "Saving CSV file...\n";
}
}
class JsonExporter extends DataExporter
{
protected function format(array $data): void
{
echo "Formatting data as JSON...\n";
}
protected function save(): void
{
echo "Saving JSON file...\n";
}
}
Usage
$exporter = new CsvExporter();
$exporter->export(['name' => 'Chris']);
How Template Method Design Pattern in PHP Improves Code Quality
The Template Method Design Pattern in PHP enforces a strict algorithm structure using a final method. This prevents subclasses from modifying the workflow order, which protects business rules. At the same time, it provides flexibility through abstract methods that subclasses must implement.
This design ensures:
- Strong separation of concerns
- Controlled extension points
- Easier testing
- Better maintainability
The parent class manages the “how” of the process, while child classes define the “what” for variable steps. This reduces duplication significantly and aligns with SOLID principles, particularly the Open/Closed Principle. You can introduce new exporters without modifying the base logic.
From a performance perspective, there is no significant overhead because everything is resolved at runtime through normal inheritance. The real advantage is structural clarity. Your code communicates intent clearly: the process is fixed, but specific operations can change.
In large PHP systems such as report engines, data pipelines, or CLI automation scripts, this pattern prevents accidental modification of critical workflows. It centralizes process control and reduces the chance of breaking changes when adding new features.
Disadvantages
- Tight coupling due to inheritance.
- Can increase class hierarchy complexity.
- Less flexible than composition-based patterns.
Conclusion
This pattern is ideal when you need consistent execution order with customizable steps. It keeps your application predictable, structured, and easy to extend.
If you are building exporters, payment systems, workflow engines, or any structured processing logic, this pattern provides a clean and maintainable approach. By defining the algorithm once and letting subclasses handle variations, you avoid duplication and enforce architectural discipline.
When used correctly, the Template Method Design Pattern in PHP becomes a powerful tool in your design pattern toolbox, especially in structured business logic layers.
Interested in More Design Patterns?
Discover other powerful patterns like Factory, Strategy, and Observer in this full guide: